Access via LOID
An LOID is a 8 byte number containing the main base number in the first 2 bytes and a consecutive database entry number in the last 6 bytes or 48 low order bits. 15 high order bits are reserved for database entry type and main base numbers. The top high order byte is a flag and reserved for internal use.
LOID
- 0xFFFF0000 in the 32 high order bytes indicates an empty entry number regardless on the remaining part of the number.
- 0x8000nnnnnnnn are numbers reserved for temporary database entries
- 0x4000nnnnnnnn are numbers reserved for transient database entries, i.e database entries stored in memory.
- 0x1000nnnnnnnn are numbers reserved for database entries in overload databases
|
Pos |
Size |
|
|
0 |
2 |
Mainbase number and entry options |
|
2 |
6 |
Entry number in main base |
Each main base manages an array, where the entry number refers to the position within this array. In order to optimize the database access, the array is organized in a hierarchical way. Each byte in the entry number defines the position of the entry number on the corresponding level.
The lowest level contains EBI instances, which provide file addresses for the database entries. As long as the database has less than 256 database entries, only one array entry on the lowest level is stored. When exceeding this number, an upper level will be created, which file addresses (64 bit) for the lower.
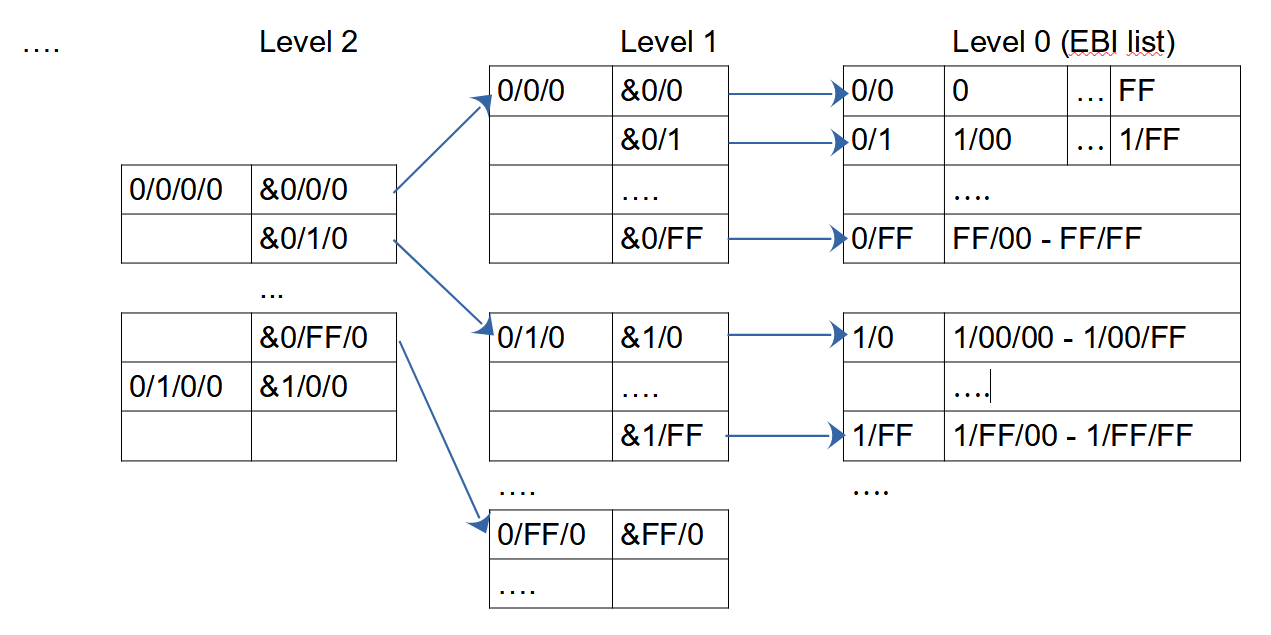
Each index entry on level 1-5 contains 256 addresses (64 bit) to the next lower level entry. In level 0 index entries, 256 EBIs are stored. The address of first index entry on each level is stored in a level table.
EBI
|
Pos |
Size |
|
|
0 |
2 |
Status bits |
|
2 |
2 |
Modification count (uint16, reset to 0 when exceeding 65535) |
|
4 |
4 |
Reserved entry length (int32) |
|
8 |
8 |
File position (64 bit access) ==> IEH |
|
8 |
8 |
File position for entry version list in case of versioning |
|
16 |
4 |
Version number for current entry (uint32) |
|
20 |
2 |
Data area number (int16) |
|
22 |
2 |
User related access rights uint16, (not used) |
The file position points to the database entry preceded by the entry header (IEH):
IEH
|
Pos |
Size |
|
|
0 |
4 |
Used entry length (int32, without IEH) |
|
4 |
2 |
Internal data type number (uint16, set when defining data type) |
|
6 |
1 |
Entry type (instance, index, part of index ...) |
|
7 |
1 |
Schema version when entry had been stored |
Data base entry's data begins immediately after the IEH.

