Persistent and Temporary Indexes
Persistent and temporary indexes are organizes in the same way. The difference is, that persistent indexes are stored permanently in the database, while temporary indexes are stored in a temporary main base which will be removed at the end of the process.
Indexes stored are organized in three different ways:
- SOME - Instance list (unordered)
- SMALL - Key list (ordered and unordered)
- LARGE - Key tree (ordered)
The structure of key lists, which appear also as bottom nodes in a key tree, depend on the unique or multiple key values property in the index definition.
 An instance list is a database entry that directly stores a number of instances. In this case, instances do not get an LOID and may be considered as a type of dynamic array. Since instances in instance lists cannot be addressed via LOID, those cannot be defined for relationships and may not contain relationship properties.
An instance list is a database entry that directly stores a number of instances. In this case, instances do not get an LOID and may be considered as a type of dynamic array. Since instances in instance lists cannot be addressed via LOID, those cannot be defined for relationships and may not contain relationship properties.
Key lists may be addressed directly as collection index (SMALL), but also as low level index in LARGE indexes.Key lists may be unique or not.
 Ordered unique key lists indexes are stored in a single database entry containing index entries that consist of the instance LOID and the key value. Key values contain one or more object type attributes according to the key definition. The maximum key length is limited to 1024. The maximum number of index entries in a key list is limited to 32767. In order to locate an index entry in a key list, binary search is performed.
Ordered unique key lists indexes are stored in a single database entry containing index entries that consist of the instance LOID and the key value. Key values contain one or more object type attributes according to the key definition. The maximum key length is limited to 1024. The maximum number of index entries in a key list is limited to 32767. In order to locate an index entry in a key list, binary search is performed.
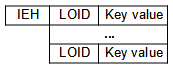
In case of not unique indexes, the key list entries in the (low level) key list point to a small unordered key list.
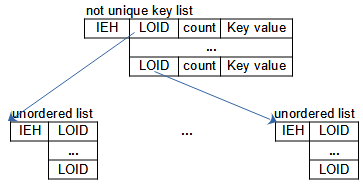
Unordered list entries do not contain key values, but the instance LOID, only, in this case to instances with the same key value. Key entries in the not unique key list contain the LOID pointing to the unordered list and the count of entries in the referenced unordered list.
Large indexes start with an icbe that contains the LOID for the top key list, which is either a bottom key list as explained above or an upper level index entry. The number of levels is also stored in the icbe. When the level is 1, the large index only contains a (bottom) key list, which may change later when adding more keys. The size for all upper level and bottom index entries is limited to 4088.
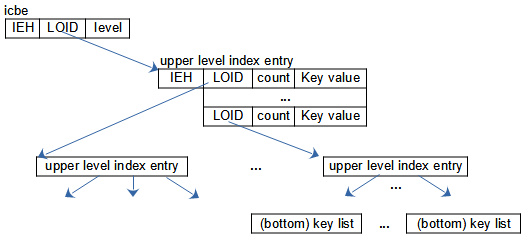
Below the icbe key trees are organized as B* trees, that contain any number of levels. Database entries for upper level index entries consist of a number of key list entries. Each upper level key list entry contains the LOID to the next lower level index entry, the total number of subordinated entries in bottom indexes (key trees), i.e. the total number of referenced instances below, and the largest key value of the next lower key list.
The bottom key list is just a simple key list where each index entry contains the instance LOID and the key value (for unique indexes) or a not unique key list with an unordered list below each entry.

