Transient Indexes
Transient indexes area created temporarily in main storage, e.g. in order to support temporarily created indexes for persistent or transient instances. In contrast to to persistent indexes, only ordered and unordered key lists are supported, regardless on the defined index type (SOME, SMALL, LARGE)
Ordered transient key lists are organized as binary trees, where each node in the tree contains the key value, total of managed bottom entries and a pointer to left (lower or equal key value) and right entry (greater or equal key value).
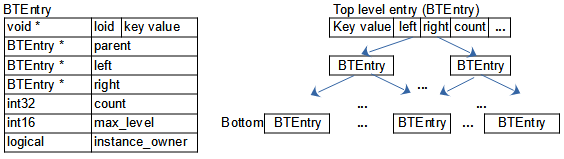
For bottom entries, the left and right pointer are null. The system keeps the tree in balance, i.e. the number of steps from top to bottom is always the same or differs only by 1. When a key has been located, the "instance" pointer refers to an area, that contains a loid and the key value. Depending on the first four high order bits, the loid may point to a transient (in memory) instance (void*), to an instance in a temporary main base (LOID with temporary main base number) or to a persistent database instance (LOID with persistent main base number).
Not unique binary trees may contain more than one entry with the same key value.
An unordered transient index is just a dynamic loid array, where an loid may point to a transient (in memory) instance (void*), to an instance in a temporary main base (LOID with temporary main base number) or to a persistent database instance (LOID with persistent main base number).

